Flood: definition and types
|
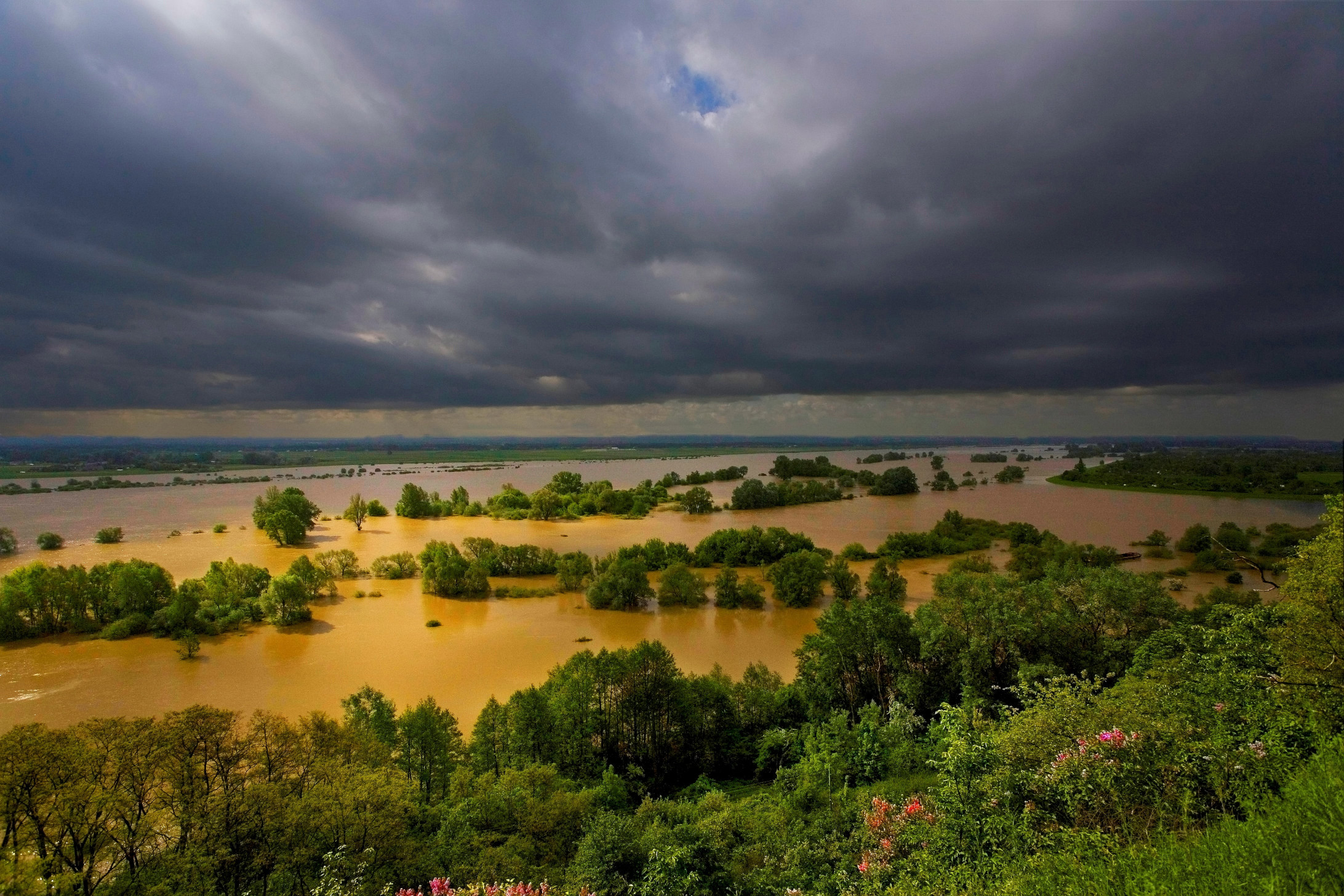
FLOOD is one of the most common natural hazards, which is a natural phenomenon of an extreme nature, often violent, occurring irregularly. In accordance with art. 16 section 43 of the Water Law of 20 July 2017, flood is defined as “a temporary coverage with water of an area not normally covered by water, in particular caused by high water in natural water-courses, reservoirs, onshore canals, excluding coverage of an area with water caused by high water in sewage systems”. |
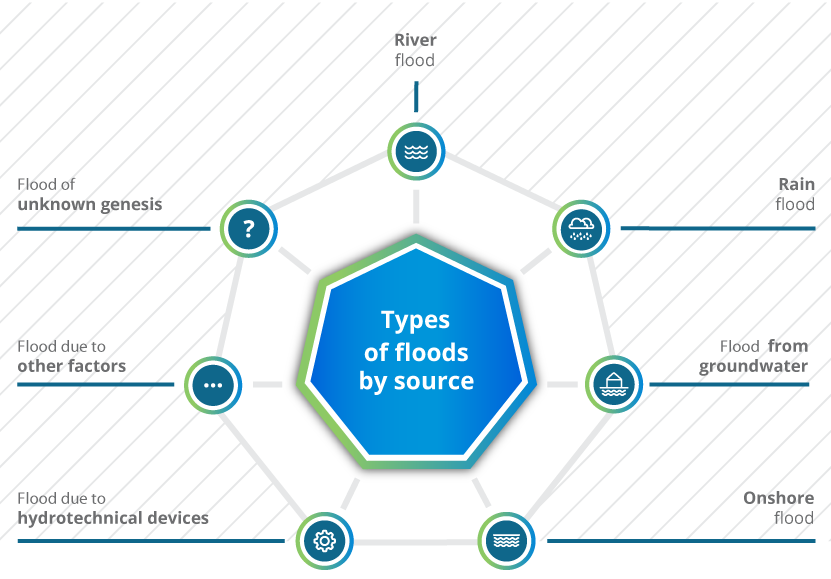 |
TYPES OF FLOODS BY SOURCE
|
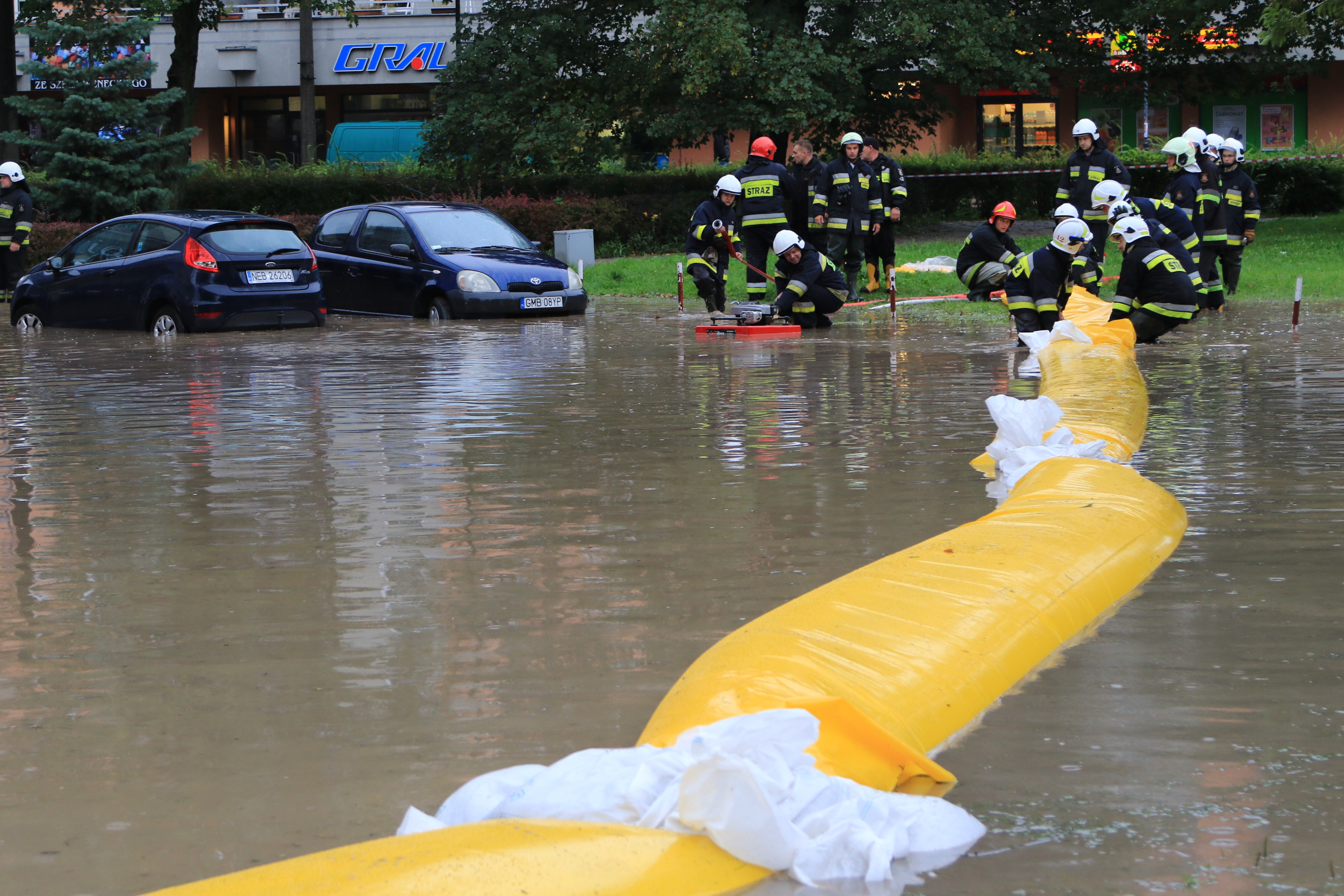
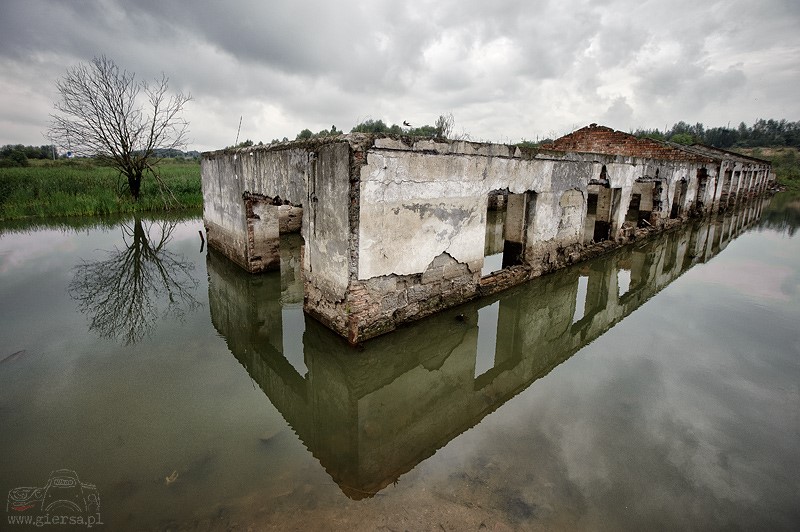
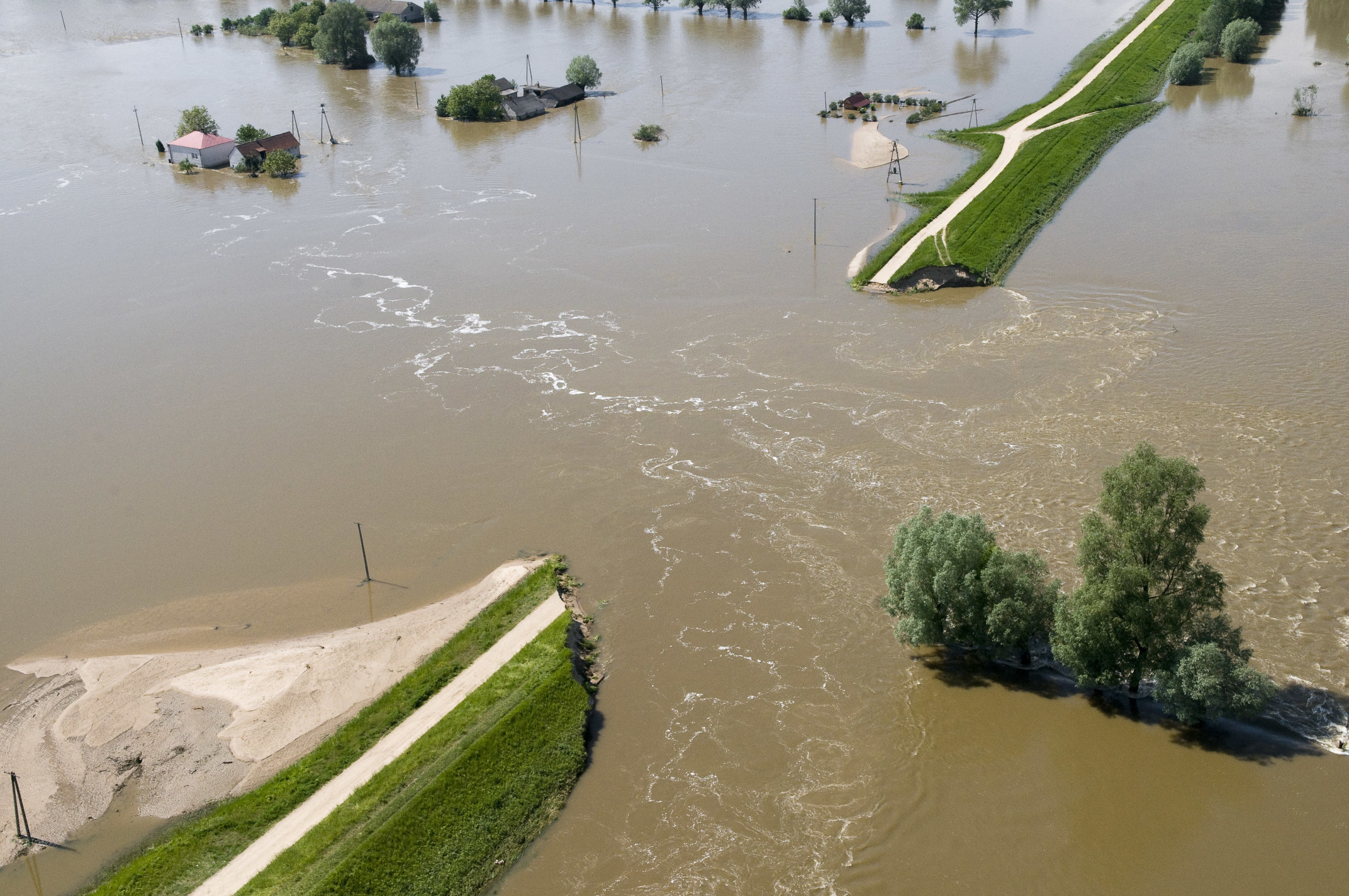
RIVER FLOOD Flood associated with high water in rivers, streams, mountain streams, canals, lakes, including floods due to melting snow. |
RAIN FLOOD Flood associated with flooding an area with water coming directly from rain or melting snow. May include urban storm water or high water in non-urban areas. |
|
|
FLOOD FROM GROUNDWATER Flood associated with flooding an area due to an increase of water level above ground level. May include an increase in ground and underground water due to the high level of surface water. |
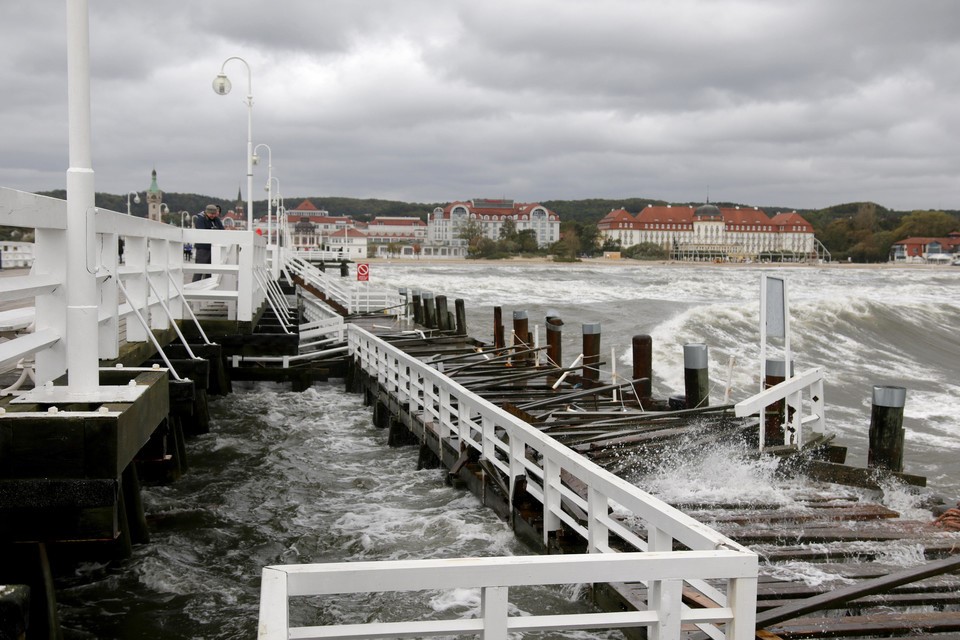
ONSHORE FLOOD Flood associated with flooding an area by marine waters, including by river mouths and coastal lakes. |
|
|
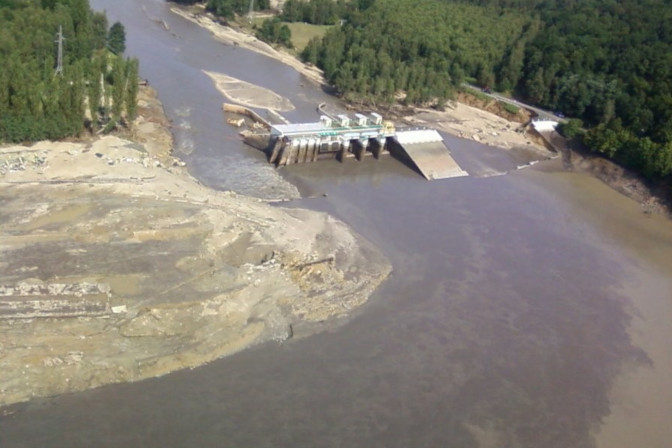
FLOOD DUE TO HYDROTECHNICAL DEVICES Flood associated with flooding an area due to failures of damming structures. |
FLOOD DUE TO OTHER FACTORS and FLOOD OF UNKNOWN GENESIS. |
TYPES OF FLOODS BY MECHANISM
|
NATURAL SWELLING Flooding of an area due to an increase of water level. |
WATER TRANSFER Through flood structures – flooding of an area due to transfer of water, e.g. through the crown of a flood bank. |
|
|
STRUCTURE FAILURE Flood or technical infrastructure – flooding of an area due to the destruction or damage or natural or technical flood banks or technical infrastructure, including failures of retention structures, wings of the floodgate. |
BLOCKAGE FLOOD Flooding of an area to the emergence of a natural or artificial blockage of a watercourse. |
There are also floods characterized by different mechanisms.
Floods are natural phenomena which cannot be prevented. However, certain human activities and climate change contribute to an increase in the likelihood of floods and in the number of their negative effects.












